|
|
In the directory with MicroServer.java
we put a simple Web page file named message.html.
We run our server application from the command line as follows:
>
java MicroServer 1234
The program can receive the port
number as an argument (on a Unix platform you should pick
a port number above 1023) or it will use the default of 2222.
Here we see the program starting and the output that results
when a page request arrives from a client:
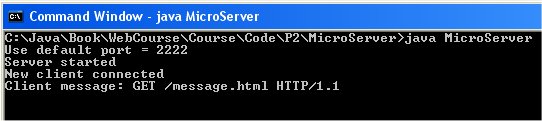
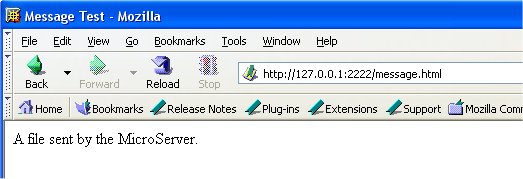
From a browser on the same machine (using the 127.0.0.1
IP address for the local machine) we can request the message
file. A browser screen capture shows:
Below we repeat the code listings again so that you can see
the two classes together:
|
|
import
java.net.*;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
/**
* An application to create a ServerSocket
object and
* spin off a threaded process to serve each
client.
**/
public class MicroServer {
public static void main (String argv[])
throws IOException {
int port; // port number
// Get the port number from
the command line.
try{
port = Integer.parseInt
(argv[0]);
} catch (Exception e) {
port = 2222; //
Default
System.out.println
("Use default port = 2222");
}
// Create a ServerSocket object
to watch that port for clients
ServerSocket server_socket =
new ServerSocket (port);
System.out.println ("Server
started");
// Loop indefinitely while waiting
for clients to connect
while (true) {
// accept () does
not return until a client requests a connection
Socket client_socket
= server_socket.accept ();
// Now that a client
has arrived, create an instance of our special
// thread subclass
to respond to it.
Worker worker =
new Worker (client_socket);
worker.start ();
System.out.println
("New client connected");
}
} // main
} // class MicroServer |
|
|
import
java.net.*;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
/** Threaded process to serve the client connected
to the socket.**/
class Worker extends Thread {
Socket fClient = null;
/** Pass the socket as a argument to
the constructor **/
Worker ( Socket client ) throws SocketException
{
fClient = client;
// Set the thread priority
down so that the ServerSocket
// will be responsive to
new clients.
setPriority ( NORM_PRIORITY
- 1 );
} // ctor
/**
* This thread
receives a message from the client that will
* request a web
page file. The file name is found relative to
* the directory
location of this code.
**/
public void run () {
try {
// Use the client
socket to obtain an input stream from it.
InputStream
socket_in = fClient.getInputStream ();
// For text
input we wrap an InputStreamReader around
// the raw input
stream and set ASCII character encoding.
InputStreamReader
isr =
new InputStreamReader (socket_in, "8859_1");
// Finally,
use a BufferReader wrapper to obtain
// buffering
and higher order read methods.
BufferedReader
client_in = new BufferedReader (isr);
// Now get an
output stream to the client.
OutputStream
client_out = fClient.getOutputStream ();
// For text
output we wrap an OutputStreamWriter around
// the raw output
stream and set ASCII character encoding.
OutputStreamWriter
osr =
new
OutputStreamWriter (client_out, "8859_1");
// Finally,
we use a PrintWriter wrapper to obtain its
// higher level
output methods.Open in autoflush mode.
// (Autoflush
occurs only with println() method.)
PrintWriter
pw_client_out = new PrintWriter (osr, true );
// First read
the message from the client
String client_str
= client_in.readLine ();
System.out.println
("Client message: "+client_str);
// Split the
message into substrings.
String [] tokens
= client_str.split(" ");
// Check that
the message has a minimun number of words
// and that
the first word is the GET command.
if ((tokens.length
>= 2) &&
tokens[0].equals ("GET")) {
String file_name = tokens[1];
//
Ignore the leading "/" on the file name.
if
(file_name.startsWith ("/"))
file_name
= file_name.substring (1);
//
If no file name is there, use index.html default.
if
(file_name.endsWith ("/") || file_name.equals (""))
file_name = file_name + "index.html";
//
Check if the file is hypertext or plain text
String
content_type;
if
(file_name.endsWith (".html") ||
file_name.endsWith
(".htm")) {
content_type = "text/html";
}
else
{
content_type
= "text/plain";
}
//
Now read the file from the disk and write it to
the
//
output stream to the client.
try
{
//
Open a stream to the file.
FileInputStream
file_in = new FileInputStream (file_name);
//
Send the header.
pw_client_out.print
("HTTP/1.0 200 OK\r\n");
File
file = new File (file_name);
Date
date = new Date (file.lastModified ());
pw_client_out.print
("Date: " + date + "\r\n");
pw_client_out.print
("Server: MicroServer 1.0\r\n");
pw_client_out.print
("Content-length: " + file_in.available ()
+
"\r\n");
pw_client_out.print
("Content-type: " + content_type
+ "\r\n\r\n");
//
Creat a byte array to hold the file.
byte
[] data = new byte [file_in.available ()];
file_in.read
(data); // Read file into
the byte array
client_out.write
(data); // Write it to client output stream
client_out.flush
(); // Remember to flush
output buffer
file_in.close
(); //
Close file input stream
}
catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
//
If no such file, then send the famous 404 message.
pw_client_out.println
("404 Object Not Found" );
}
} else{
pw_client_out.println
("400 Bad Request");
}
} catch (IOException e)
{
System.out.println
( "I/O error " + e );
}
// Close client socket.
try {
fClient.close
();
} catch (IOException e){
System.out.println
("I/O error " + e );
}
// On return from run ()
the thread process will stop.
} // run
} // class Worker
|
References &
Web Resources
Latest update: Dec. 15, 2004
|
|
|



